In a Brønsted-Lowry acid-base reaction, a conjugate acid is the species formed after the base accepts a proton. By contrast, a conjugate base is the species formed after an acid donates its proton. The two species in a conjugate acid-base pair have the same molecular formula except the acid has an extra H + compared to the conjugate base.
2021 HSC Chemistry Exam Paper Solutions ⚗️
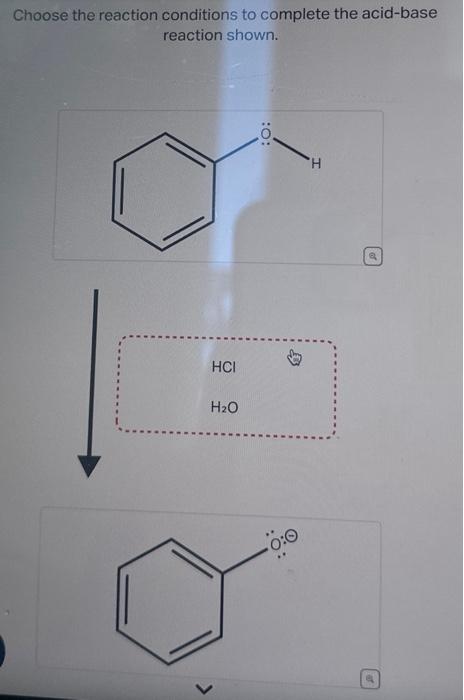
Science Chemistry Chemistry questions and answers + Choose the reaction conditions to complete the acid-base reaction shown. HCI H₂O :O: Ö:0 H o This problem has been solved! You’ll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. See Answer

Source Image: blog.addgene.org
Download Image
Worked example: Calculating the pH after a weak acid-strong base reaction (excess acid) Weak base-strong acid reactions. Weak acid-weak base reactions. Acid-base reactions. Science > AP®︎/College Chemistry > … Choose 1 answer: Choose 1 answer: (Choice A) HBr (a q) and NH A 3 (a q)
Source Image: lubio.ch
Download Image
Solved Choose the reaction conditions to complete the | Chegg.com Chemistry Chemistry questions and answers Choose the reaction conditions to complete the acid-base reaction shown. This problem has been solved! You’ll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. See Answer Question: Choose the reaction conditions to complete the acid-base reaction shown.
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Choose The Reaction Conditions To Complete The Acid-Base Reaction Shown
Chemistry Chemistry questions and answers Choose the reaction conditions to complete the acid-base reaction shown. This problem has been solved! You’ll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. See Answer Question: Choose the reaction conditions to complete the acid-base reaction shown. The reaction between an acid and a base is called an acid-base reaction or a neutralization reaction. Although acids and bases have their own unique chemistries, the acid and base cancel each other’s chemistry to produce a rather innocuous substance—water. In fact, the general acid-base reaction is.
Solved Choose the reaction conditions to complete the | Chegg.com
Answer e. 4.3: Acid-Base Reactions is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. An acidic solution and a basic solution react together in a neutralization reaction that also forms a salt. Acid-base reactions require both an acid and a base. In Brønsted-Lowry …. Precipitation reactions: Video, Anatomy & Definition | Osmosis

Source Image: osmosis.org
Download Image
Reaction Mechanism of Glycoside Hydrolase Family 116 Utilizes Perpendicular Protonation | ACS Catalysis Answer e. 4.3: Acid-Base Reactions is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. An acidic solution and a basic solution react together in a neutralization reaction that also forms a salt. Acid-base reactions require both an acid and a base. In Brønsted-Lowry ….

Source Image: pubs.acs.org
Download Image
2021 HSC Chemistry Exam Paper Solutions ⚗️ In a Brønsted-Lowry acid-base reaction, a conjugate acid is the species formed after the base accepts a proton. By contrast, a conjugate base is the species formed after an acid donates its proton. The two species in a conjugate acid-base pair have the same molecular formula except the acid has an extra H + compared to the conjugate base.

Source Image: matrix.edu.au
Download Image
Solved Choose the reaction conditions to complete the | Chegg.com Worked example: Calculating the pH after a weak acid-strong base reaction (excess acid) Weak base-strong acid reactions. Weak acid-weak base reactions. Acid-base reactions. Science > AP®︎/College Chemistry > … Choose 1 answer: Choose 1 answer: (Choice A) HBr (a q) and NH A 3 (a q)

Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Acid Catalyzed Hydration Concept & Examples – Lesson | Study.com Science Chemistry Choose the reaction conditions to complete the acid-base reaction shown. A: CH3CO2H B: NaOH, H2O C: NaH, THF D: NaOCH2CH3, CH3CH2OH E: [ (CH3)2CH]2N- Choose the reaction conditions to complete the acid-base reaction shown. A: CH3CO2H B: NaOH, H2O C: NaH, THF D: NaOCH2CH3, CH3CH2OH E: [ (CH3)2CH]2N-

Source Image: study.com
Download Image
Polymers | Free Full-Text | Optimizing PET Glycolysis with an Oyster Shell-Derived Catalyst Using Response Surface Methodology Chemistry Chemistry questions and answers Choose the reaction conditions to complete the acid-base reaction shown. This problem has been solved! You’ll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. See Answer Question: Choose the reaction conditions to complete the acid-base reaction shown.

Source Image: mdpi.com
Download Image
Chemical Indicators: Definition, Types and Examples The reaction between an acid and a base is called an acid-base reaction or a neutralization reaction. Although acids and bases have their own unique chemistries, the acid and base cancel each other’s chemistry to produce a rather innocuous substance—water. In fact, the general acid-base reaction is.

Source Image: geeksforgeeks.org
Download Image
Reaction Mechanism of Glycoside Hydrolase Family 116 Utilizes Perpendicular Protonation | ACS Catalysis
Chemical Indicators: Definition, Types and Examples Science Chemistry Chemistry questions and answers + Choose the reaction conditions to complete the acid-base reaction shown. HCI H₂O :O: Ö:0 H o This problem has been solved! You’ll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. See Answer
Solved Choose the reaction conditions to complete the | Chegg.com Polymers | Free Full-Text | Optimizing PET Glycolysis with an Oyster Shell-Derived Catalyst Using Response Surface Methodology Science Chemistry Choose the reaction conditions to complete the acid-base reaction shown. A: CH3CO2H B: NaOH, H2O C: NaH, THF D: NaOCH2CH3, CH3CH2OH E: [ (CH3)2CH]2N- Choose the reaction conditions to complete the acid-base reaction shown. A: CH3CO2H B: NaOH, H2O C: NaH, THF D: NaOCH2CH3, CH3CH2OH E: [ (CH3)2CH]2N-